Second and third class levers are differentiated by __________. – Second and third class levers are differentiated by their unique characteristics, including the position of the fulcrum, effort, and load. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending the principles of levers and their diverse applications in various fields.
Levers are simple machines that amplify force or change the direction of a force. They consist of a rigid bar pivoted on a fixed point called the fulcrum. By applying effort at one point of the lever, a load can be lifted or moved at another point.
Second and Third Class Levers

Levers are simple machines that consist of a rigid bar pivoted on a fixed point, called a fulcrum. The input force, or effort, is applied to one end of the lever, while the output force, or load, is applied to the other end.
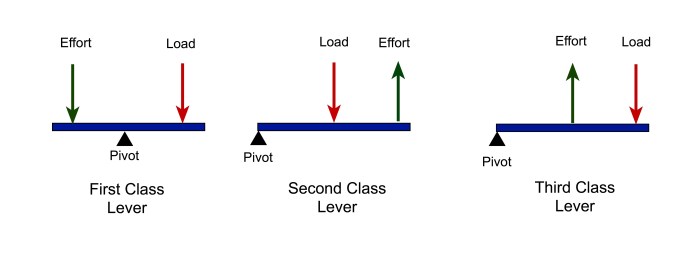
Levers are classified into three classes based on the relative positions of the fulcrum, effort, and load.
Differentiating Second and Third Class Levers
Second and third class levers are differentiated by the position of the fulcrum, effort, and load.
- Second class lever:The fulcrum is located between the effort and the load. The effort is applied to one end of the lever, and the load is applied to the other end. The load is always greater than the effort.
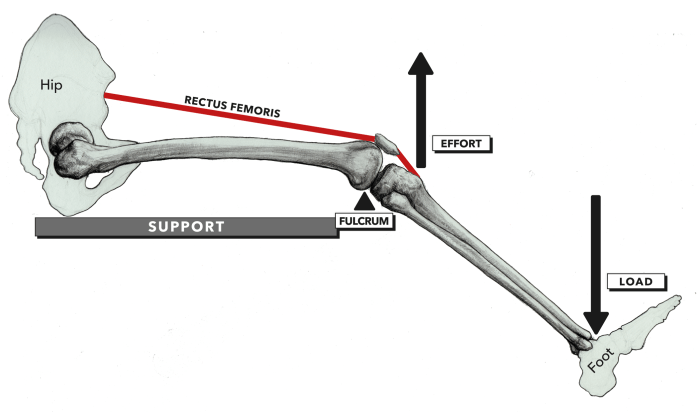
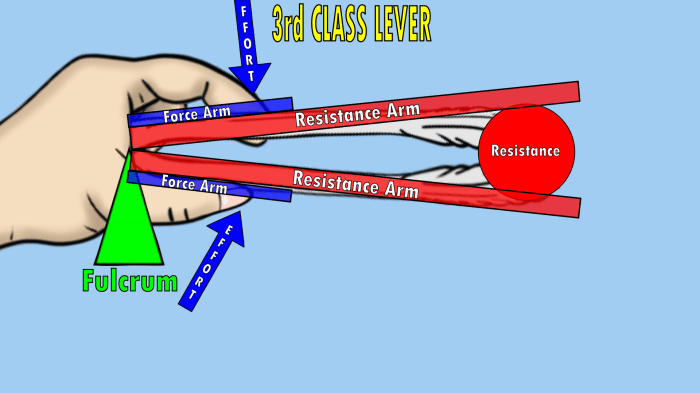
- Third class lever:The fulcrum is located at one end of the lever. The effort is applied to the other end of the lever, and the load is located between the effort and the fulcrum. The effort is always greater than the load.
Applications of Second and Third Class Levers
Second and third class levers are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Second class lever:Wheelbarrow, nutcracker, bottle opener
- Third class lever:Fishing rod, tweezers, tongs
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Class, Second and third class levers are differentiated by __________.
Each class of lever has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Second class lever:
- Advantages:Amplifies the input force, making it easier to lift heavy loads
- Disadvantages:The load must always be greater than the effort
- Third class lever:
- Advantages:Amplifies the input force, making it easier to move objects with precision
- Disadvantages:The effort must always be greater than the load
Essential FAQs: Second And Third Class Levers Are Differentiated By __________.
What is the primary difference between second and third class levers?
In second class levers, the load is placed between the fulcrum and the effort, while in third class levers, the effort is placed between the fulcrum and the load.
Can you provide an example of a second class lever?
A wheelbarrow is a common example of a second class lever, where the load (the weight of the contents) is placed between the fulcrum (the wheel) and the effort (the force applied to the handles).
What is a real-world application of a third class lever?
Fishing rods are a practical example of third class levers, where the effort (the force applied to the rod) is placed between the fulcrum (the angler’s hand) and the load (the weight of the fish).