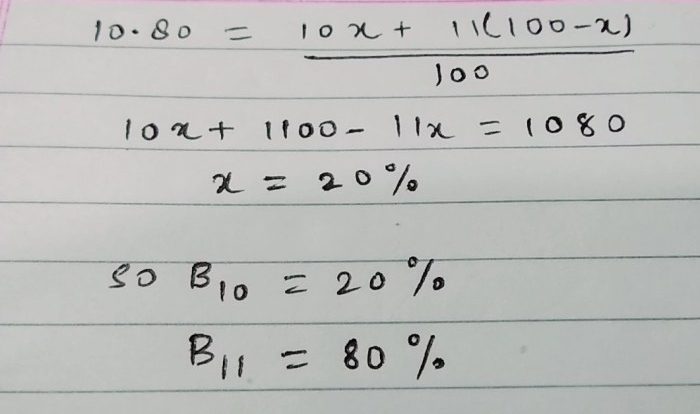Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity Kotz embarks on an illuminating journey, delving into the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of matter. From the highly reactive to the inert, this exploration unveils the intricate interplay between chemical bonding, reaction mechanisms, and thermodynamics, shaping the reactivity and dynamics of the chemical world.
At the heart of this narrative lies the concept of chemical reactivity, a measure of a substance’s propensity to undergo chemical transformations. Factors such as temperature, concentration, and surface area modulate reactivity, influencing the rates and pathways of reactions. Delving deeper, the text elucidates the relationship between chemical bonding and reactivity, revealing how bond strength and type dictate the susceptibility of molecules to react.
Chemical Reactivity

Chemical reactivity refers to the propensity of a substance to undergo chemical change. It is a measure of how easily a substance can participate in a chemical reaction. Highly reactive substances are those that readily undergo chemical reactions, while unreactive substances are those that do not react easily.
Factors Affecting Chemical Reactivity
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, making them more likely to collide and react.
- Concentration: Higher concentrations of reactants increase the likelihood of collisions, leading to a faster reaction rate.
- Surface area: Increasing the surface area of a reactant increases the number of molecules exposed to each other, resulting in a faster reaction rate.
Chemical Bonding and Reactivity: Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity Kotz

Chemical bonding plays a crucial role in determining the reactivity of a substance. The strength and type of bonds formed between atoms affect the stability of the molecule and its susceptibility to chemical change.
Bond Strength and Reactivity
- Stronger bonds require more energy to break, making the molecule less reactive.
- Weaker bonds are easier to break, resulting in a more reactive molecule.
Reaction Mechanisms
Reaction mechanisms describe the step-by-step process by which reactants are converted into products. Different types of reaction mechanisms exist, each with its own characteristics and implications for the rate and selectivity of the reaction.
Nucleophilic Substitution and Electrophilic Addition
- Nucleophilic substitutioninvolves the replacement of a leaving group by a nucleophile (an electron-rich species).
- Electrophilic additioninvolves the addition of an electrophile (an electron-deficient species) to a double or triple bond.
Thermodynamics and Reactivity
Thermodynamics deals with the energy changes associated with chemical reactions. The concepts of enthalpy, entropy, and free energy are crucial in understanding the spontaneity and direction of reactions.
Enthalpy, Entropy, and Free Energy
- Enthalpy(H) represents the heat absorbed or released during a reaction.
- Entropy(S) measures the randomness or disorder of a system.
- Free energy(G) combines enthalpy and entropy to determine the spontaneity of a reaction.
Kinetics and Reactivity
Kinetics studies the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence them. The reaction rate is the change in concentration of reactants or products over time.
Reaction Rate, Rate Law, and Activation Energy
- Reaction ratemeasures the speed of a reaction.
- Rate lawexpresses the mathematical relationship between the reaction rate and the concentrations of reactants.
- Activation energyis the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur.
Applications of Chemical Reactivity
Chemical reactivity finds numerous applications in various fields, including:
Industry, Medicine, and Environmental Science, Chemistry and chemical reactivity kotz
- Industry:Chemical reactivity is essential for the production of materials, fuels, and pharmaceuticals.
- Medicine:Understanding chemical reactivity is crucial for drug design and development.
- Environmental science:Chemical reactivity plays a role in pollution control and environmental remediation.
Helpful Answers
What is the concept of chemical reactivity?
Chemical reactivity refers to the tendency of a substance to undergo chemical transformations, forming new substances.
How does temperature affect chemical reactivity?
Increasing temperature generally increases chemical reactivity by providing more energy to overcome activation barriers.
What is the relationship between chemical bonding and reactivity?
Chemical bonding influences reactivity by determining the strength and type of bonds within a molecule, affecting its susceptibility to react.