Que es mejor consolidar deudas o bancarrota – In the realm of personal finance, the question of whether to consolidate debts or file for bankruptcy often arises. This article delves into the intricacies of both options, examining their financial implications, legal procedures, and long-term consequences. By exploring the pros and cons of each approach, we aim to provide individuals with a comprehensive understanding to make informed decisions regarding their financial well-being.
Debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single, more manageable loan. Bankruptcy, on the other hand, is a legal proceeding that discharges or reorganizes debts, offering a fresh financial start. Both options have their unique advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on individual circumstances and financial goals.
Financial Overview: Que Es Mejor Consolidar Deudas O Bancarrota
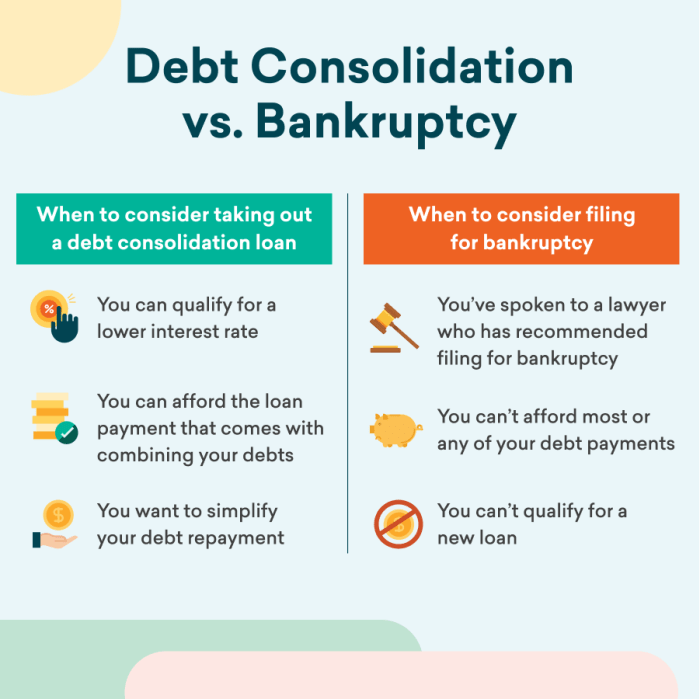
Debt consolidation and bankruptcy are two distinct financial strategies that can impact individuals’ financial well-being significantly. Understanding the implications of each option is crucial for making informed decisions. Debt consolidation involves consolidating multiple debts into a single loan or account, typically with a lower interest rate.
This can simplify debt management, reduce monthly payments, and improve credit scores over time.
Bankruptcy, on the other hand, is a legal process that allows individuals to discharge or restructure their debts. It can provide immediate relief from overwhelming debt, but it also has severe consequences for creditworthiness and long-term financial stability. Filing for bankruptcy can result in a significant drop in credit scores, making it difficult to obtain future credit, loans, or employment.
Debt Consolidation Methods
Various debt consolidation methods are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Balance transfer credit cards allow individuals to transfer high-interest debts to a new card with a lower interest rate, often for a limited time. Personal loans can also be used for debt consolidation, providing a fixed interest rate and repayment period.
Debt management plans, offered by non-profit credit counseling agencies, involve working with creditors to negotiate lower interest rates and monthly payments.
- Advantages of Debt Consolidation:
- Simplified debt management
- Reduced monthly payments
- Improved credit scores (over time)
- Disadvantages of Debt Consolidation:
- Potential for higher interest rates on new loans
- Fees associated with consolidation (e.g., balance transfer fees)
- May not address underlying financial issues
Bankruptcy Procedures, Que es mejor consolidar deudas o bancarrota
There are two main types of bankruptcy available to individuals: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. Chapter 7 bankruptcy involves liquidating non-exempt assets to pay off creditors. It provides a quick discharge of debts but can result in the loss of valuable property.
Chapter 13 bankruptcy allows individuals to restructure their debts and repay them over a period of time, typically 3-5 years. This option preserves assets but requires a steady income and adherence to the repayment plan.
- Advantages of Bankruptcy:
- Immediate relief from overwhelming debt
- Discharge of certain debts
- Disadvantages of Bankruptcy:
- Severe damage to credit scores
- Difficulty obtaining future credit
- Potential loss of assets (Chapter 7)
Impact on Creditworthiness
Both debt consolidation and bankruptcy can have a significant impact on creditworthiness. Debt consolidation can improve credit scores over time by reducing credit utilization and making payments on time. However, taking on new debt can temporarily lower scores. Bankruptcy, on the other hand, has a severe negative impact on credit scores, which can persist for up to 10 years.
It makes it difficult to obtain future credit, loans, or employment.
- Tips for Rebuilding Credit After Debt Consolidation or Bankruptcy:
- Make all payments on time
- Reduce credit utilization
- Build a positive credit history with a secured credit card or credit-builder loan
- Dispute any errors on credit reports
Alternatives to Debt Consolidation and Bankruptcy
In some cases, alternatives to debt consolidation and bankruptcy may be available. Debt counseling and credit counseling provide personalized guidance and support to individuals struggling with debt. Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the amount owed, but it can damage credit scores and is not always successful.
- Advantages of Alternatives:
- May avoid the negative consequences of debt consolidation or bankruptcy
- Can provide personalized support and guidance
- Disadvantages of Alternatives:
- May not be suitable for all situations
- Can be time-consuming and require significant effort
FAQ
What are the key differences between debt consolidation and bankruptcy?
Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan, while bankruptcy discharges or reorganizes debts through a legal proceeding.
How does debt consolidation affect credit scores?
Debt consolidation can initially lower credit scores due to inquiries and new accounts, but responsible management can lead to long-term improvements.
What are the long-term consequences of bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy can remain on credit reports for up to 10 years and may limit access to credit and employment opportunities.

