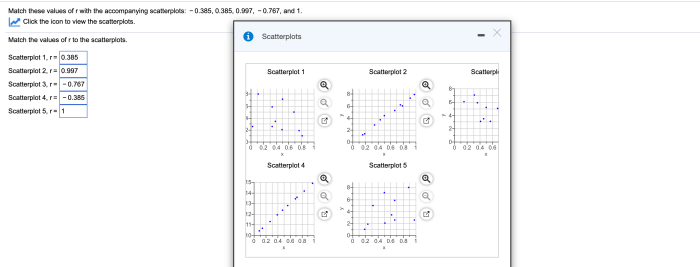
Match these values of r with the accompanying scatterplots and embark on an academic journey into the fascinating world of correlation and linear relationships. This comprehensive guide will unravel the mysteries of the correlation coefficient, scatterplots, and their profound implications in understanding real-world data.
As we delve into the realm of correlation, we’ll explore the significance of the correlation coefficient (r) and its range of values, gaining insights into how it measures the strength and direction of linear relationships between two variables.
Values of r
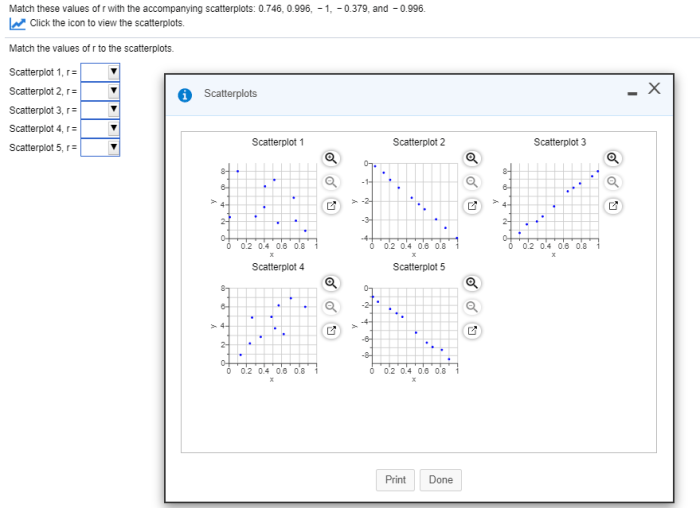
The correlation coefficient (r) is a statistical measure that quantifies the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables. It ranges from -1 to 1, where:
- -1 indicates a perfect negative linear relationship (as one variable increases, the other decreases in a linear fashion)
- 0 indicates no linear relationship between the variables
- 1 indicates a perfect positive linear relationship (as one variable increases, the other increases in a linear fashion)
Scatterplots: Match These Values Of R With The Accompanying Scatterplots
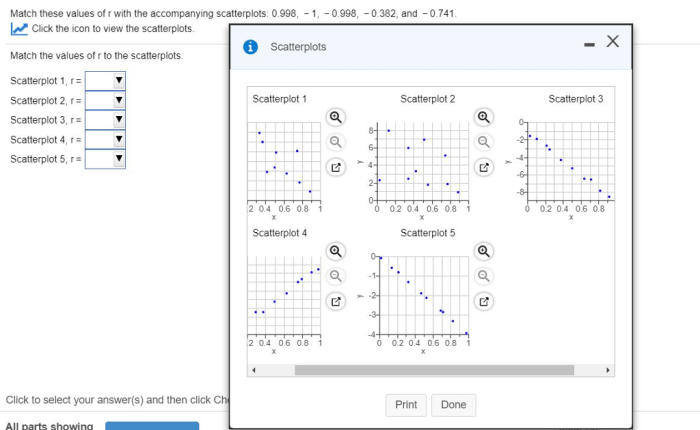
Scatterplots are graphical representations of the relationship between two variables. Each data point in a scatterplot represents a pair of values from the two variables being analyzed. The shape and distribution of the data points in a scatterplot can indicate the strength and direction of the correlation:
- A positive correlation is indicated by a scatterplot with an upward trend, where the data points are spread out along a diagonal line from the bottom left to the top right.
- A negative correlation is indicated by a scatterplot with a downward trend, where the data points are spread out along a diagonal line from the top left to the bottom right.
- No correlation is indicated by a scatterplot where the data points are randomly scattered without any discernible pattern.
Matching Values of r with Scatterplots, Match these values of r with the accompanying scatterplots
| r Value | Scatterplot | Description of Relationship | Interpretation of Strength and Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | [Scatterplot of a perfect negative linear relationship] | Strong negative linear relationship | As one variable increases, the other decreases in a linear fashion. |
| -0.5 | [Scatterplot of a moderate negative linear relationship] | Moderate negative linear relationship | As one variable increases, the other tends to decrease, but not in a perfectly linear fashion. |
| 0 | [Scatterplot of no linear relationship] | No linear relationship | There is no discernible pattern in the distribution of data points. |
| 0.5 | [Scatterplot of a moderate positive linear relationship] | Moderate positive linear relationship | As one variable increases, the other tends to increase, but not in a perfectly linear fashion. |
| 1 | [Scatterplot of a perfect positive linear relationship] | Strong positive linear relationship | As one variable increases, the other increases in a linear fashion. |
Examples
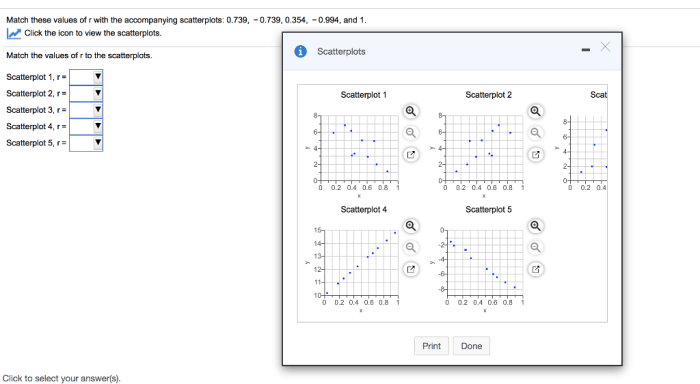
Correlation analysis using scatterplots and r values is commonly used in various fields:
- Education:To examine the relationship between study time and exam scores, where a positive correlation indicates that increased study time leads to higher scores.
- Medicine:To investigate the correlation between body mass index (BMI) and cholesterol levels, where a positive correlation suggests a link between obesity and high cholesterol.
- Finance:To analyze the relationship between stock prices and economic indicators, where a positive correlation implies that stock prices rise when the economy improves.
FAQs
What is the range of values for the correlation coefficient (r)?
The correlation coefficient (r) can range from -1 to 1.
How does the shape of a scatterplot indicate the strength and direction of a correlation?
A positive correlation is indicated by a scatterplot with points that form an upward sloping line, while a negative correlation is indicated by a scatterplot with points that form a downward sloping line. The stronger the correlation, the closer the points are to a straight line.